Convert from Roman (Rom) to Decimal (Base 10)
Perform the conversion of numbers between different numerical systems.
Roman (Rom) = Decimal (Base 10)
Information about conversion units:
About Roman (Rom)
The Roman numeral system is an ancient numeric system that was used in the Roman Empire. In this system, letters are used to represent numbers, with the most commonly used letters being I, V, X, L, C, D, and M. Each letter has a specific numeric value, and they are combined in certain ways to form numbers. Unlike the decimal system, the Roman numeral system doesn't have a native representation of zero. That means there is no specific symbol for zero in the Roman numeral system. Despite this, the Roman numeral system is still used in some contexts, such as numbering years in certain calendars.
About Decimal (Base 10)
The Decimal Number System is a positional numeral system and is the system that we all use without realizing why. The Decimal System uses 10 digits (from 0 to 9). By combining these digits, larger numbers can be expressed.
Roman (Rom) vs Decimal (Base 10)
| Roman (Rom) | Decimal (Base 10) |
|---|---|
| I | 1 |
| IV | 4 |
| V | 5 |
| IX | 9 |
| X | 10 |
| XL | 40 |
| L | 50 |
| XC | 90 |
| C | 100 |
| CD | 400 |
| D | 500 |
| CM | 900 |
| M | 1000 |
| IV | 4000 |
| V | 5000 |
| IX | 9000 |
| X | 10000 |
| XL | 40000 |
| L | 50000 |
| XC | 90000 |
| C | 100000 |
| CD | 400000 |
| D | 500000 |
| CM | 900000 |
| M | 1000000 |
¿How to convert from Roman (Rom) to Decimal (Base 10)?
Note: To convert a number in the Roman numeral system to any other base, we first need to convert the Roman numeral to decimal (base 10). Follow these steps:
Roman Numerals and Their Basic Rules.
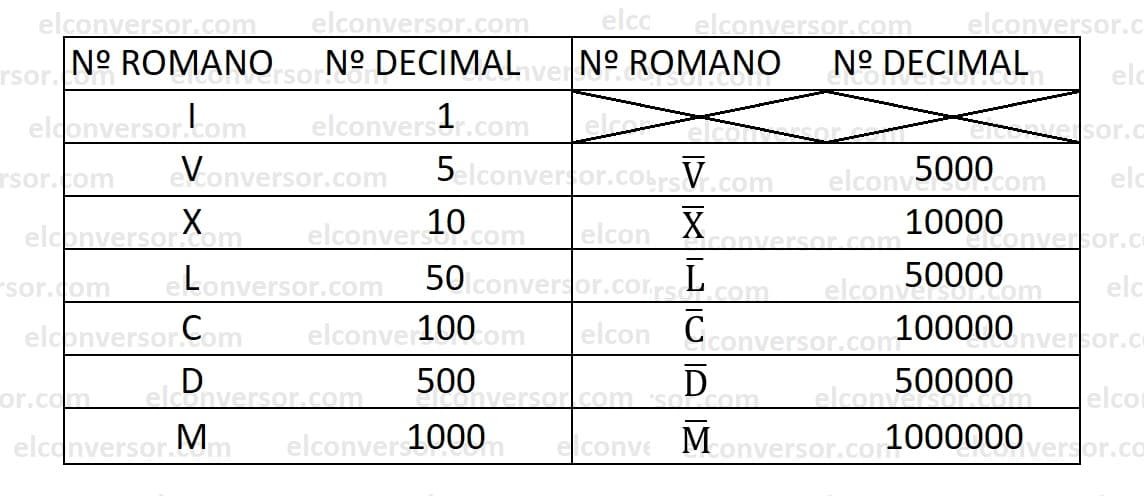
- The Roman numerals I, X, C, and M can be repeated up to three times when writing a composite Roman numeral.
- The Roman numerals V, L, and D cannot be repeated.
- If a composite Roman numeral has a smaller number to the right than to the left, then both are added. Example: XI: The number on the right (I = 1) is smaller than on the left (X = 10), so they are added, i.e., XI = 11.
- If a composite Roman numeral has a larger number to the right and it is I, X, or C, then the left is subtracted from the right. Example: IX: The number on the right (X = 10) is larger than on the left (I = 1), and it's I, so the left is subtracted from the right, i.e., IX = 9.
- If a Roman numeral has a line over it, its value is multiplied by a thousand. Example: IX
: the number is 9,000, as it's the Roman numeral representing 9 and the line over it multiplies it by a thousand.
Applying the steps to the Roman numeral "CLIX":
- C = 100, L = 50, I = 1, X = 10
- We observe I = 1 before X = 10, so I is subtracted from X;
- Add 100 + 50 + (10 - 1) = 159.
The Roman numeral "CLIX" is equivalent to 159 in decimal.

Conversion table of Roman (Rom) to Decimal (Base 10)
| Roman (Rom) | Decimal (Base 10) |
|---|---|
| I | 1 |
| II | 2 |
| III | 3 |
| IV | 4 |
| V | 5 |
| VI | 6 |
| VII | 7 |
| VIII | 8 |
| IX | 9 |
| X | 10 |
| XI | 11 |
| XII | 12 |
| XIII | 13 |
| XIV | 14 |
| XV | 15 |
| XVI | 16 |
| XVII | 17 |
| XVIII | 18 |
| XIX | 19 |
| XX | 20 |
| XXI | 21 |
| XXII | 22 |
| XXIII | 23 |
| XXIV | 24 |
| XXV | 25 |
| XXVI | 26 |
| XXVII | 27 |
| XXVIII | 28 |
| XXIX | 29 |
| XXX | 30 |
| XXXI | 31 |
| XXXII | 32 |
| XXXIII | 33 |
| XXXIV | 34 |
| XXXV | 35 |
| XXXVI | 36 |
| XXXVII | 37 |
| XXXVIII | 38 |
| XXXIX | 39 |
| XL | 40 |
| XLI | 41 |
| XLII | 42 |
| XLIII | 43 |
| XLIV | 44 |
| XLV | 45 |
| XLVI | 46 |
| XLVII | 47 |
| XLVIII | 48 |
| XLIX | 49 |
| L | 50 |
| LI | 51 |
| LII | 52 |
| LIII | 53 |
| LIV | 54 |
| LV | 55 |
| LVI | 56 |
| LVII | 57 |
| LVIII | 58 |
| LIX | 59 |
| LX | 60 |
| LXI | 61 |
| LXII | 62 |
| LXIII | 63 |
| LXIV | 64 |
| LXV | 65 |
| LXVI | 66 |
| LXVII | 67 |
| LXVIII | 68 |
| LXIX | 69 |
| LXX | 70 |
| LXXI | 71 |
| LXXII | 72 |
| LXXIII | 73 |
| LXXIV | 74 |
| LXXV | 75 |
| LXXVI | 76 |
| LXXVII | 77 |
| LXXVIII | 78 |
| LXXIX | 79 |
| LXXX | 80 |
| LXXXI | 81 |
| LXXXII | 82 |
| LXXXIII | 83 |
| LXXXIV | 84 |
| LXXXV | 85 |
| LXXXVI | 86 |
| LXXXVII | 87 |
| LXXXVIII | 88 |
| LXXXIX | 89 |
| XC | 90 |
| XCI | 91 |
| XCII | 92 |
| XCIII | 93 |
| XCIV | 94 |
| XCV | 95 |
| XCVI | 96 |
| XCVII | 97 |
| XCVIII | 98 |
| XCIX | 99 |
| C | 100 |
| CI | 101 |
| CII | 102 |
| CIII | 103 |
| CIV | 104 |
| CV | 105 |
| CVI | 106 |
| CVII | 107 |
| CVIII | 108 |
| CIX | 109 |
| CX | 110 |
| CXI | 111 |
| CXII | 112 |
| CXIII | 113 |
| CXIV | 114 |
| CXV | 115 |
| CXVI | 116 |
| CXVII | 117 |
| CXVIII | 118 |
| CXIX | 119 |
| CXX | 120 |
| CXXI | 121 |
| CXXII | 122 |
| CXXIII | 123 |
| CXXIV | 124 |
| CXXV | 125 |
| CXXVI | 126 |
| CXXVII | 127 |
| CXXVIII | 128 |
| CXXIX | 129 |
| CXXX | 130 |
| CXXXI | 131 |
| CXXXII | 132 |
| CXXXIII | 133 |
| CXXXIV | 134 |
| CXXXV | 135 |
| CXXXVI | 136 |
| CXXXVII | 137 |
| CXXXVIII | 138 |
| CXXXIX | 139 |
| CXL | 140 |
| CXLI | 141 |
| CXLII | 142 |
| CXLIII | 143 |
| CXLIV | 144 |
| CXLV | 145 |
| CXLVI | 146 |
| CXLVII | 147 |
| CXLVIII | 148 |
| CXLIX | 149 |
| CL | 150 |
| CLI | 151 |
| CLII | 152 |
| CLIII | 153 |
| CLIV | 154 |
| CLV | 155 |
| CLVI | 156 |
| CLVII | 157 |
| CLVIII | 158 |
| CLIX | 159 |
| CLX | 160 |
| CLXI | 161 |
| CLXII | 162 |
| CLXIII | 163 |
| CLXIV | 164 |
| CLXV | 165 |
| CLXVI | 166 |
| CLXVII | 167 |
| CLXVIII | 168 |
| CLXIX | 169 |
| CLXX | 170 |
| CLXXI | 171 |
| CLXXII | 172 |
| CLXXIII | 173 |
| CLXXIV | 174 |
| CLXXV | 175 |
| CLXXVI | 176 |
| CLXXVII | 177 |
| CLXXVIII | 178 |
| CLXXIX | 179 |
| CLXXX | 180 |
| CLXXXI | 181 |
| CLXXXII | 182 |
| CLXXXIII | 183 |
| CLXXXIV | 184 |
| CLXXXV | 185 |
| CLXXXVI | 186 |
| CLXXXVII | 187 |
| CLXXXVIII | 188 |
| CLXXXIX | 189 |
| CXC | 190 |
| CXCI | 191 |
| CXCII | 192 |
| CXCIII | 193 |
| CXCIV | 194 |
| CXCV | 195 |
| CXCVI | 196 |
| CXCVII | 197 |
| CXCVIII | 198 |
| CXCIX | 199 |
| CC | 200 |
| CCI | 201 |
| CCII | 202 |
| CCIII | 203 |
| CCIV | 204 |
| CCV | 205 |
| CCVI | 206 |
| CCVII | 207 |
| CCVIII | 208 |
| CCIX | 209 |
| CCX | 210 |
| CCXI | 211 |
| CCXII | 212 |
| CCXIII | 213 |
| CCXIV | 214 |
| CCXV | 215 |
| CCXVI | 216 |
| CCXVII | 217 |
| CCXVIII | 218 |
| CCXIX | 219 |
| CCXX | 220 |
| CCXXI | 221 |
| CCXXII | 222 |
| CCXXIII | 223 |
| CCXXIV | 224 |
| CCXXV | 225 |
| CCXXVI | 226 |
| CCXXVII | 227 |
| CCXXVIII | 228 |
| CCXXIX | 229 |
| CCXXX | 230 |
| CCXXXI | 231 |
| CCXXXII | 232 |
| CCXXXIII | 233 |
| CCXXXIV | 234 |
| CCXXXV | 235 |
| CCXXXVI | 236 |
| CCXXXVII | 237 |
| CCXXXVIII | 238 |
| CCXXXIX | 239 |
| CCXL | 240 |
| CCXLI | 241 |
| CCXLII | 242 |
| CCXLIII | 243 |
| CCXLIV | 244 |
| CCXLV | 245 |
| CCXLVI | 246 |
| CCXLVII | 247 |
| CCXLVIII | 248 |
| CCXLIX | 249 |
| CCL | 250 |
| CCLI | 251 |
| CCLII | 252 |
| CCLIII | 253 |
| CCLIV | 254 |
| CCLV | 255 |
| CCLVI | 256 |
| CCLVII | 257 |
| CCLVIII | 258 |
| CCLIX | 259 |
| CCLX | 260 |
| CCLXI | 261 |
| CCLXII | 262 |
| CCLXIII | 263 |
| CCLXIV | 264 |
| CCLXV | 265 |
| CCLXVI | 266 |
| CCLXVII | 267 |
| CCLXVIII | 268 |
| CCLXIX | 269 |
| CCLXX | 270 |
| CCLXXI | 271 |
| CCLXXII | 272 |
| CCLXXIII | 273 |
| CCLXXIV | 274 |
| CCLXXV | 275 |
| CCLXXVI | 276 |
| CCLXXVII | 277 |
| CCLXXVIII | 278 |
| CCLXXIX | 279 |
| CCLXXX | 280 |
| CCLXXXI | 281 |
| CCLXXXII | 282 |
| CCLXXXIII | 283 |
| CCLXXXIV | 284 |
| CCLXXXV | 285 |
| CCLXXXVI | 286 |
| CCLXXXVII | 287 |
| CCLXXXVIII | 288 |
| CCLXXXIX | 289 |
| CCXC | 290 |
| CCXCI | 291 |
| CCXCII | 292 |
| CCXCIII | 293 |
| CCXCIV | 294 |
| CCXCV | 295 |
| CCXCVI | 296 |
| CCXCVII | 297 |
| CCXCVIII | 298 |
| CCXCIX | 299 |
| CCC | 300 |